
Do Tattoos Cause Cancer?
Do tattoos have become increasingly popular as a form of self-expression and body art, with millions of people worldwide sporting intricate designs on their skin. Amidst this trend, however, questions have arisen regarding the potential health risks associated with tattoos, including concerns about ingredients in tattoo inks and speculation about whether tattoos increase the risk of cancer. Let’s delve into the research and provide valuable insight into whether tattoo ink is toxic or carcinogenic.
Understanding the Tattooing Process and Its Implications
To determine if there is causation or coincidence between tattoos and cancer, we must first understand the tattooing process. Tattooing involves depositing ink into the dermis layer of the skin using a bundle of needles. In most modern cases, tattoo artists use a specialised machine equipped with one or more needles to puncture the skin at a rapid pace, depositing the ink beneath the outer layer of the skin.
Throughout the process, tattoo artists carefully control the depth and pressure of the needle to ensure the ink is deposited evenly and accurately. Once the tattoo is complete, the skin may undergo a period of healing, during which a scab forms and eventually peels away, revealing the permanent design beneath. This process can and often does produce varying results, as tattoo artists can range from having little to no experience to decades of experience, which is why it’s important to consult with your potential tattoo artist before getting a tattoo.
Potential Health Risks Associated with Tattoos
Common Tattoo Ink Ingredients
When considering the tattooing process and any associated health risks, it’s important to take into account the ingredients in the tattoo ink. Common ingredients found in tattoo inks can vary depending on the brand and colour, but some typical components include:
- Pigments (derived from minerals, metals, or synthetic compounds). This includes chemicals like manganese which can be harmful to the lungs, liver, and kidneys, with symptoms similar to Parkinson’s Disease (such as shaking or trembling, stiffness, and slow motor movement).
- Carrier fluids (such as purified water, alcohol, or glycerin). While common carrier fluids often include non-hazardous elements, they can also contain harmful chemicals like methanol, which, although not known to cause cancer, is still toxic and damaging to the body.
- Solvents (including ethanol, propylene glycol, or denatured alcohol)
- Additives (such as preservatives, stabilizers, and thickeners)
- Contaminants (e.g., trace amounts of heavy metals like lead, cadmium, and mercury). Cadmium, which is known to cause cancers, can appear as a contaminant or as a pigment. Cadmium can target the heart, gastrointestinal system, neurological functions, and the reproductive and respiratory systems, causing permanent damage.
Since tattoo inks are not regulated by the FDA, there is no set standard for tattoo inks. Because of this, adverse reactions can occur, including allergic reactions or more serious injuries.
Long Term Effects of Tattoos
Regarding the long-term effects of tattoos, factors such as size, location, ink quality, and individual health play a significant role. Considering the future of your tattoo may also be worthwhile. Given concerns about whether tattoo inks can damage the organs, it’s important to consider the effects of removing tattoos as well. Laser tattoo removal pushes potentially harmful inks into the body’s lymphatic system to be processed out over time, but Tatt2Away’s natural tattoo removal method removes ink up and out of the skin, eliminating risks associated with metals passing through the lymphatic system. If tattoo removal isn’t a future consideration, there are still some potential long-term effects of tattoos that you should be aware of.
- Fading: Over time, tattoos may fade due to exposure to sunlight, aging skin, and the body’s natural regeneration processes. Vibrant colours may become dull, and fine details may blur.
- Skin Changes: The skin around tattoos may undergo changes such as stretching, wrinkling, or sagging, particularly if the tattoo is located in an area prone to weight fluctuations or aging effects.
- Allergic Reactions: Some people may develop allergic reactions to tattoo ink, resulting in itching, redness, swelling, or other skin irritations. These reactions can occur immediately after getting a tattoo or years later.
- Infection: Improper tattooing techniques or inadequate aftercare can increase the risk of infection. Infections may manifest as redness, warmth, pus, or fever and can lead to more severe complications if left untreated.
- Granulomas and Keloids: In some cases, the body may react to tattoo ink by forming granulomas (small nodules of inflamed tissue) or keloids (raised, thickened scars) around the tattoo site. These can impact the integrity of the tattoo/ink and cause damage to the skin.
- MRI Complications: Certain tattoo pigments containing metal components may cause discomfort or skin irritation during magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. Additionally, some tattoos may interfere with the accuracy of MRI results.
- Potential Health Risks: While research is ongoing, there are concerns about the long-term health effects of tattoo ink ingredients, particularly regarding their potential to migrate within the body and accumulate in organs or lymph nodes. Some studies have suggested associations between tattoos and increased risks of certain health conditions.
Cancer as a long-term effect of tattoos or tattoo inks is still being researched, but we have compiled existing data to correlate any links between the two.
Examining the Research – Skin Cancer
So, the question remains, do tattoos cause cancer?
One case study researched six individuals with skin cancer on or around a tattooed area to determine if there was any link between their tattoos and the malignant melanoma. It was determined that there was no direct cause between the skin cancer and the tattoo. Furthermore, it was concluded that there are likely not enough determining factors to decipher whether skin cancer could be caused by harmful components in tattoo ink or from sun exposure.
These findings were corroborated by another study that tested 50 cases of skin cancer on tattoos. The findings state that “The number of skin cancers arising in tattoos is seemingly low, and this association has to be considered thus far as coincidental.”
Though there may be harmful ingredients contained in tattoo ink, it is unlikely that the components can cause skin cancer.
Examining the Evidence – Other Forms of Cancer
While the risk of a direct causation between tattoo ink and skin cancer seems to be low, another study suggests there could be a loose correlation between other forms of cancer and tattoo inks due to the carcinogens found in some inks. When receiving a tattoo, ink is placed in the dermis of the skin, where over time, your body’s macrophages attempt to remove the foreign object—tattoo ink—by transporting it to the lymph nodes, which contributes to the fading of tattoos over time. Since some tattoo inks contain harmful chemicals, this could potentially lead to cancer in other parts of the body, such as the bladder or liver.
While there is speculation about this, more research is needed to definitively establish causation. If cancer from tattoos is a concern for you, make sure to consult with your tattoo artist ahead of your tattooing session to ensure that the ink they are using complies with EU standards.
Tattoo Removal and Cancer
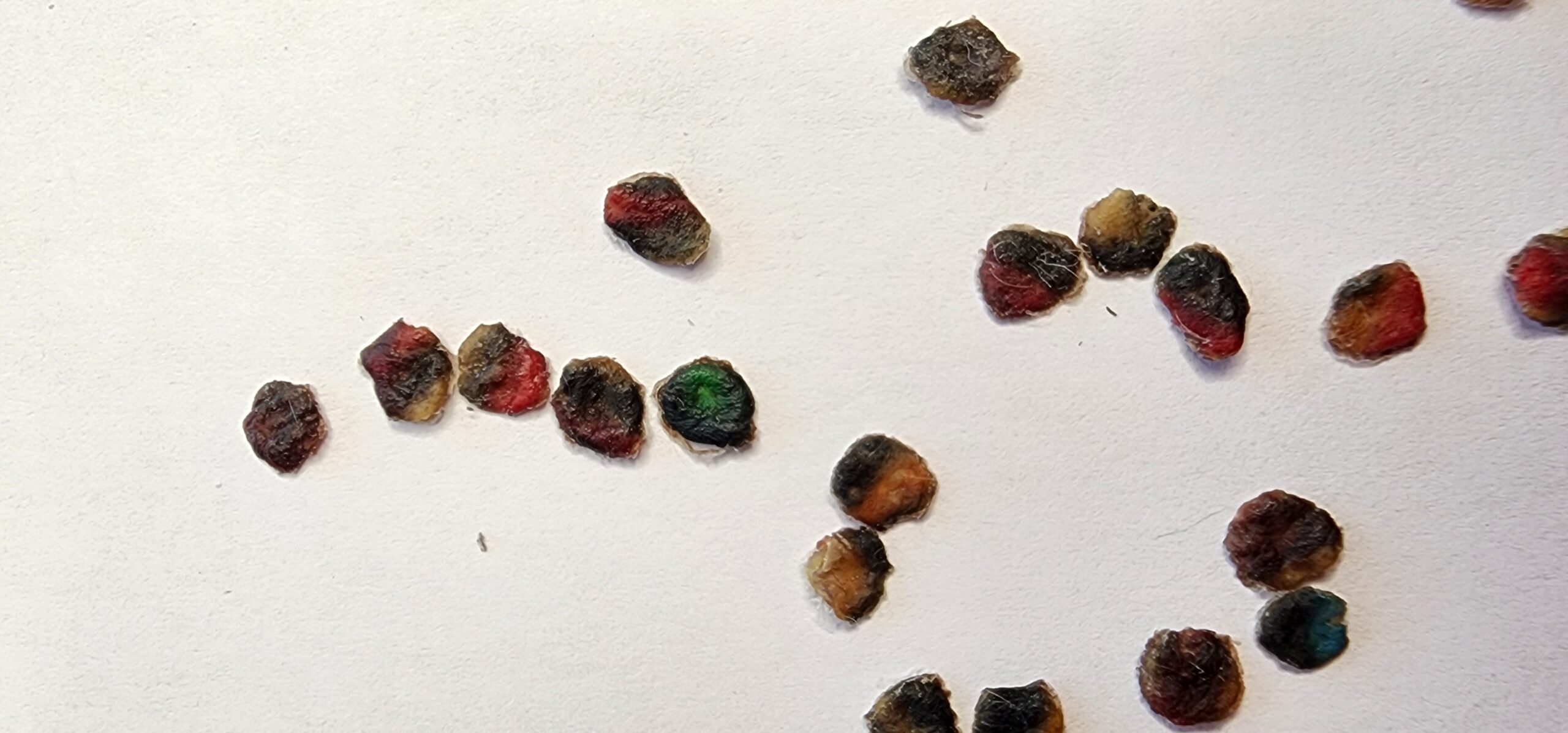
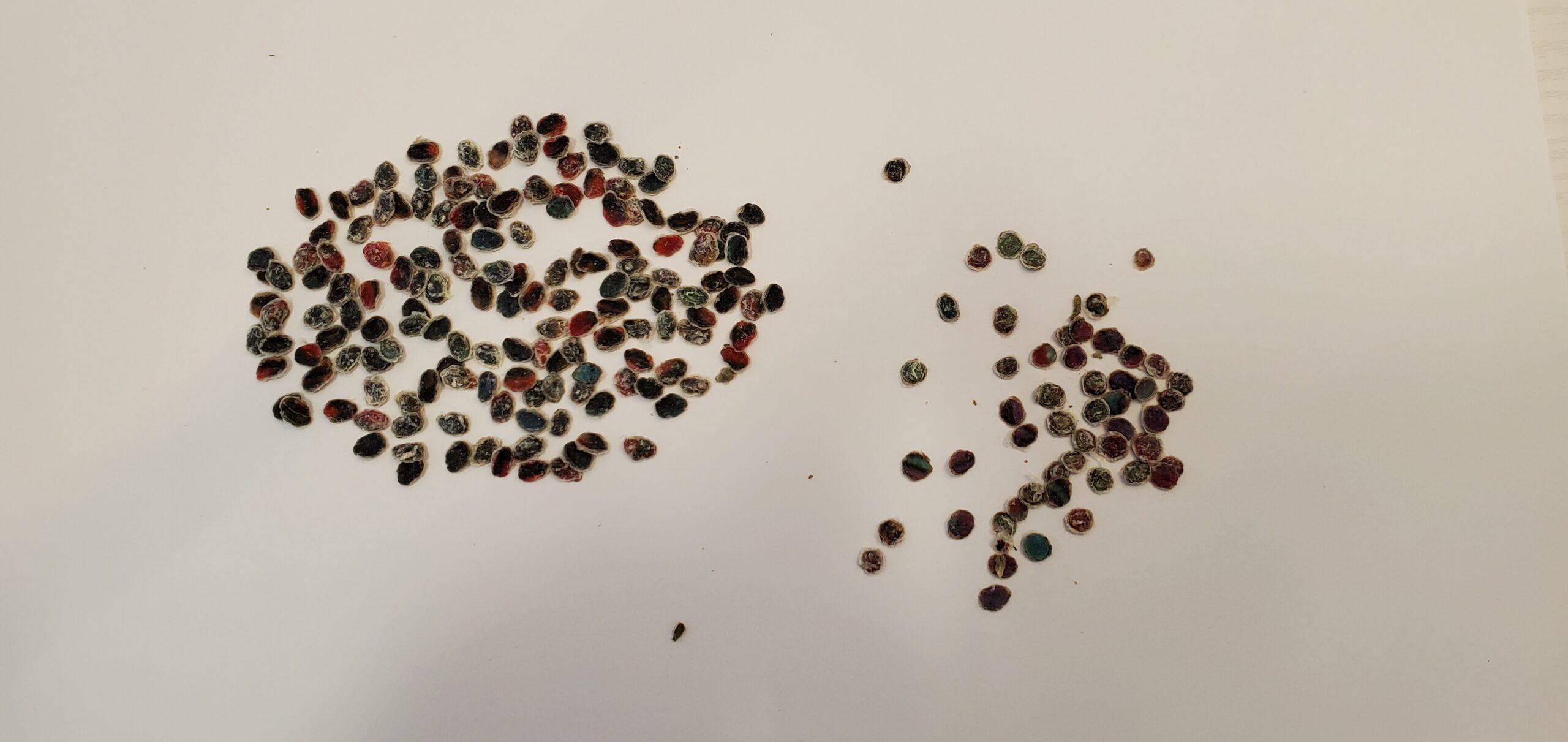


Following the line of thought that the harmful ingredients in tattoo ink could potentially cause cancer in some parts of the body, tattoo removal should also be considered. Since the body naturally tries to remove ink from a tattoo (but is ultimately unsuccessful because the ink particles are too large when placed properly), it’s important to note that laser tattoo removal works by shattering the ink into smaller pieces, allowing the body’s macrophages to process the now broken-down ink out through the lymphatic system. This means that most or all of your tattoo and its potentially harmful chemicals are processed through the lymphatic system. This could potentially cause additional harm to important organs, though minimal research has been conducted on this topic.
On contrast to the laser removal method, Tatt2Away is a tattoo removal method that removes an unwanted tattoo by lifting the ink up and out of the skin through the body’s natural healing process of scabbing. A microdermabrasion technique is applied over the tattoo, which causes a scab to form a few weeks after treatment. When the scab falls off, it pulls the ink out with it, thus eliminating any risk of processing the tattoo through the lymphatic system. Check out the pictures below to see the results of this process. To learn more about Tatt2Away, check out how organic tattoo removal works.
Ink and Health: The Final Verdict On Whether Tattoos Cause Cancer
While there is no direct link between skin cancer and tattoo inks, the presence of potentially harmful substances in tattoo ink warrants further research to ensure there are no connections between other forms of cancer and tattoos. To fully understand the potential risks of tattoos causing cancer, more studies need to be conducted.
To ensure health and safety when getting a tattoo, it’s important to follow best practices, such as proper aftercare and monitoring for any unusual reactions, to keep your body art looking its best and safest. Staying informed about potential risks is crucial so you can make well-informed decisions about tattoos and your overall well-being. For the latest tattoo removal news visit our blog.

